Zinc oxide and titanium dioxide are the only mineral compounds approved by the FDA for use as active sunscreen ingredients. But how do they compare? Which is better? Read on to explore the differences between titanium dioxide vs. zinc oxide and discover which ingredient offers superior protection.
Regarding titanium dioxide vs. zinc oxide, zinc oxide is the better choice in most aspects, except cost. Zinc oxide is more expensive but provides more comprehensive protection. Let's break down the comparison into three critical areas: sun protection, chemistry, and human and marine biology impact.
UV Protection
UV rays are categorized as UVA and UVB. UVB rays primarily affect the skin's surface, causing burns, while UVA rays penetrate deeper, contributing to premature aging. Broad-spectrum sunscreen protects against both types, ensuring comprehensive coverage.
Zinc Oxide
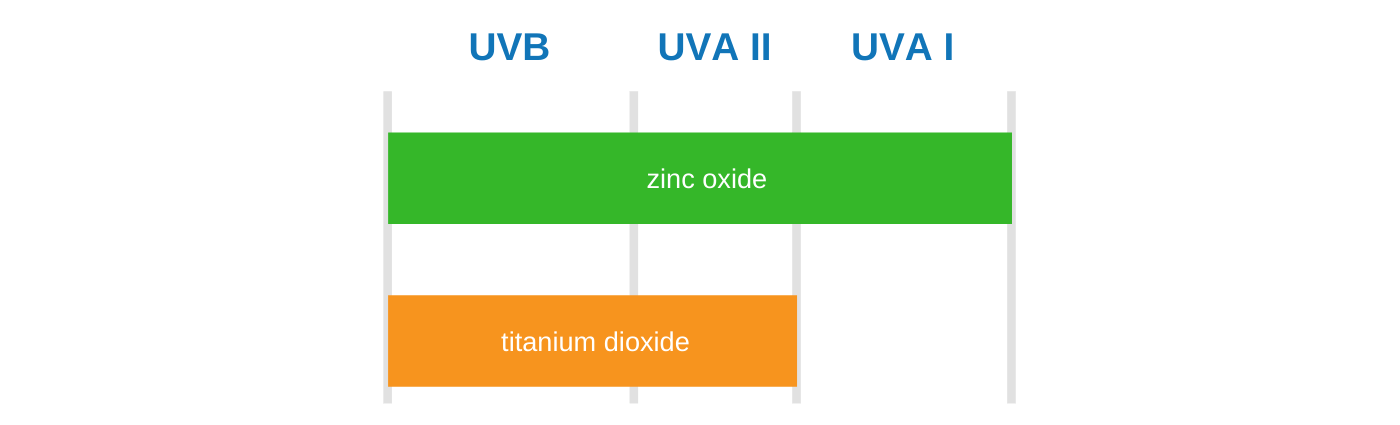
Zinc oxide is the most effective mineral sunscreen available, offering full-spectrum protection against UVA and UVB rays. It absorbs UV radiation and converts it to heat, safely radiating it away from the skin. Unlike titanium dioxide, zinc oxide provides robust coverage across both short and long ultraviolet A (UVA) wavelengths. As a standalone sunscreen ingredient, zinc oxide effectively covers the entire UVA/UVB spectrum, making it an exceptional choice for those seeking reliable sun protection products.
👉 Try our Natural Sunscreen Stick with 25% non-nano zinc oxide.
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide works by absorbing and scattering UV rays. While it effectively blocks UVB rays, its protection against UVA rays is less comprehensive. It performs poorly against long UVA rays (UVA I) and requires combining other ingredients, such as chemical sunscreen agents or zinc oxide, for broader coverage. Products relying solely on titanium dioxide often leave users vulnerable to UVA damage while preventing the natural cues of sunburn.
Chemistry
Zinc Oxide
Zinc oxide (ZnO) is derived from zinc, an essential mineral recognized as safe for use in many applications, including multivitamins. Most zinc oxide is produced by oxidizing zinc ore at high temperatures. It's an inorganic, water-insoluble compound with antimicrobial properties, ideal for sensitive skin. Non-nano zinc oxide prevents skin penetration and minimizes the creation of free radicals, ensuring safe and effective UV protection. Its stability under UV exposure makes it a cornerstone of high-quality sunscreen products.
👉 Try our Tinted Facial Sunscreen with 25% non-nano zinc oxide.
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is derived from titanium, a heavy metal with potential toxicity. It is produced through industrial processes involving ilmenite or rutile ores. While stable under most conditions, titanium dioxide becomes less stable under UV radiation, generating free radicals that can damage skin cells and accelerate aging. Non-nano titanium dioxide is safer, but nano-sized particles have raised concerns about potential health and environmental risks.

Impact on Human and Marine Biology
Zinc Oxide
Zinc oxide is gentle on sensitive skin, making it a go-to ingredient for sun protection. It is the only active sunscreen ingredient approved for infants under six months old. Non-nano zinc oxide is environmentally friendly; its particles settle on the seafloor and avoid disrupting marine ecosystems. Unlike chemical sunscreens, it does not contribute to coral bleaching or harm marine life.
Titanium Dioxide
Titanium dioxide does not play a natural role in human biology. Nano-sized titanium dioxide particles are classified as potentially carcinogenic and threaten marine life. Research indicates that titanium dioxide nanoparticles can cause oxidative stress and coral bleaching, impacting marine ecosystems. However, non-nano titanium dioxide is a safer alternative, as its larger particles do not penetrate the skin or disrupt marine systems.

Conclusion
When comparing titanium dioxide vs. zinc oxide, non-nano zinc oxide is superior for sun protection and environmental safety. While non-nano titanium dioxide is a viable option, it falls short of the comprehensive protection zinc oxide offers. Always check the labels of your sunscreen product to ensure it contains non-nano zinc oxide or titanium dioxide. Avoid products marketed as "sheer" or "clear," as these often use nano-sized particles that can penetrate the skin and harm marine life.
Choosing the right sunscreen offers more than just protection against UVA and UVB rays; it's a step toward safeguarding your health and preserving our oceans. Make informed choices and opt for sun protection products that benefit both you and the environment.




































































